- DroidAfrica
- OnePlus
- OnePlus 8 Pro
OnePlus 8 Pro
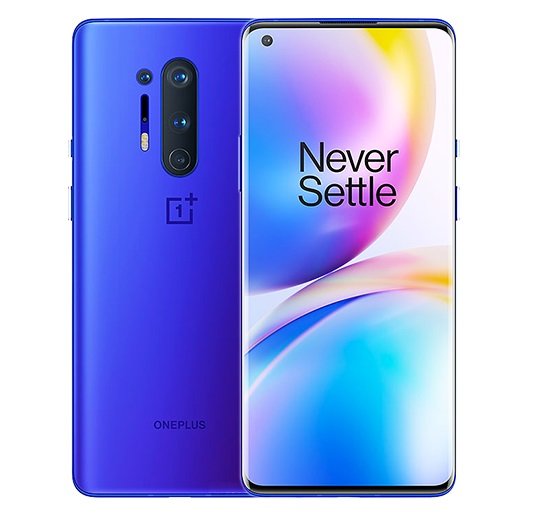

OnePlus 8 Pro Highlights and Overview
The OnePlus 8 Pro is the higher variant of the standard OnePlus 8. The major difference between the two is that the Pro version has a larger display, of course has a bigger battery with wireless charger and provide more camera fun than the standard version, aside which other things remain same. To star with, the phone has a larger 6.78-inches display, with same Fluid AMOLED panel, but has a higher 1440 x 3168 pixels resolution, and a higher 120Hz refresh rate, instead of the 90Hz used in the standard OP8.
The device draw strength from same octa-core Qualcomm Snapdragon 865 chip, clocked at 2.84GHz along with Adreno 650 GPU. Storage options includes 8/12 GB RAM and 128/256 GB non-expandable storage.
As for the camera, the OnePlus 8 Pro has four camera modules at the back. The main sensor remains a 48-megapixel lens with f/1.8 aperture, omnidirectional PDAF, Laser Autofocus and Optical Image Stabilization (OIS). The other three sensors at the back includes a 48-megapixel ultra-wide lens, 8-megapixel telephoto lens with up to 3x optical zoom, and a fourth 5-megapixel depth sensing lens. Upfront, is same 16-megapixel selfie sensor, supporting auto HDR and f/2.5 aperture.
There is a built-in 4510 mAh battery with 30W wired and wireless fast charger. You are also getting an in-display optical fingerprint scanner with dual Nano-SIM having 5G and 4G network support. It is available in Glacial Green, Ultramarine Blue and Onyx Black colors and run on the latest Android 10 with OxygenOS 10 out of the box. The full specifications and features of the OnePlus 8 Pro smartphone are detailed in the table below.
OnePlus 8 Pro Full Specifications and Features
NETWORK
| Technology | GSM / CDMA / HSPA / LTE / 5G |
| 2G Network Bands |
GSM 850 / 900 / 1800 / 1900 - SIM 1 & SIM 2 CDMA 800 / 1900 & TD-SCDMA |
| 3G Network Bands | HSDPA 850 / 900 / 1700(AWS) / 1900 / 2100 |
| 4G Network Bands | LTE band 1(2100), 2(1900), 3(1800), 4(1700/2100), 5(850), 7(2600), 8(900), 12(700), 13(700), 17(700), 18(800), 19(800), 20(800), 25(1900), 26(850), 28(700), 29(700), 30(2300), 32(1500) 34(2000), 38(2600), 39(1900), 40(2300), 41(2500), 42(3500), 46(5200), 48, 66(1700/2100), 71(600) - Global LTE Bands |
| 5G Network Bands | 5G band 1(2100), 2(1900), 3(1800), 5(850), 41(2500), 7(2600), 28(700), 66(1700), 71(600), 78(3500), 79(4700); SA/NSA - Global 5G Bands |
| Speed | HSPA 42.2/5.76 Mbps, LTE-A (5CA) Cat18 1200/150 Mbps, 5G 7.5 Gbps DL |
LAUNCH
| Also Known As |
- - |
BODY
| Dimensions | 165.3 x 74.4 x 8.5 mm |
| Weight | 199 grams |
| Build |
Glass front (Gorilla Glass) - Glass back (Gorilla Glass) - Aluminum frame - IP68 dust/water resistant |
| SIM Type | Dual SIM (Nano-SIM, dual stand-by) |
DISPLAY
| Display Type | Fluid AMOLED capacitive touchscreen, 1 Billion colors |
| Size | 6.78 inches, 111.7 cm2 (~90.8% screen-to-body ratio) |
| Resolution | 1440 x 3168 pixels, 20:9 ratio (~512 ppi density) |
PLATFORM
| Operating System | Android 10.0; OxygenOS 10.0 |
| Chipset | Qualcomm SM8250 Snapdragon 865 (7 nm+) |
| CPU | Octa-core (1x2.84 GHz Kryo 585 & 3x2.42 GHz Kryo 585 & 4x1.8 GHz Kryo 585) |
| GPU | Qualcomm Adreno 650 |
MEMORY
| RAM + ROM | 8/12 GB |
| Card Slot | No |
MAIN CAMERA
| Camera Type | Quadruple Lenses |
| Camera Sensor(s) | 48 MP + 48 MP + 8 MP + 5 MP Main camera |
| Camera Features |
Autofocus Continuous shooting Digital zoom Digital image stabilization Optical image stabilization Geotagging Panorama HDR Touch focus Face detection White balance settings ISO settings Exposure compensation Self-timer Scene mode RAW Sensor size - 1/2" Pixel size - 1.6 μm (4-in-1 pixel binning) Phase detection Focal length (35 mm equivalent) - 27 mm 1080p @ 240 fps 720p @ 480 fps Secondary sensor: 48 MP, (ultrawide), PDAF Third sensor: 8 MP Telephoto lens Fourth sensor: 5 MP, f/2.4, (depth) |
| Video Resolution | 2160p@30/60fps, 1080p@30/60/240fps, Auto HDR, gyro-EIS |
SELFIE CAMERA
| Camera Type | Single Lens |
| Camera Sensor(s) | 16 MP selfie camera |
| Camera Features |
Auto-HDR, Panorama, F/2.5 aperture |
| Video Resolution | 1080p@30fps |
SOUND
| Loudspeaker | Yes |
| Speaker Location | Chin, blow the screen |
| Audio Jack Type | No |
CONNECTIVITY
| Bluetooth | Bluetooth 5.1, A2DP, LE, aptX HD |
| NFC | |
| GPS | Yes, with dual-band A-GPS, GLONASS, BDS, GALILEO, SBAS |
| FM Radio | No |
BATTERY
| Battery Capacity | Non-removable Li-Po 4510 mAh battery |
| Wireless Charging |
Yes: Fast wireless charging 30W - Reverse wireless charging 3W |
| Talk Time Talk Time is the longest time that a single battery charge will last when you are constantly talking on the phone under perfect conditions, Ambient temperature and highly dependent on the cellular network environment such as the distance to the closest cell network tower. | Up to 31 hours |
| Stand-by | Up to 590 hours |
OTHER FEATURES
| Sensors | Fingerprint (side-mounted), accelerometer, proximity, compass |
| Box Contents | Charging Brick / USB cable |
OnePlus 8 Pro User Reviews and Opinions
Disclaimer Note
This specification was entered manually, hence we CANNOT guarantee 100% accuracy. Any error? Let us know in the comment section.







































Leave a Reply